A fake Pixelmon NFT site entices fans with free tokens and collectibles while infecting them with malware that steals their cryptocurrency wallets.
Pixelmon is a popular NFT project whose roadmap includes creating an online metaverse game where you can collect, train, and battle other players using pixelmon pets.
With close to 200,000 Twitter followers and over 25,000 Discord members, the project has garnered a lot of interest.
Impersonating the Pixelmon project
To take advantage of this interest, threat actors have copied the legitimate pixelmon.club website and created a fake version at pixelmon[.]pw to distribute malware.
This site is almost a replica of the legitimate site, but instead of offering a demo of the project's game, the malicious site offers executables that install password-stealing malware on a device.
Source: BleepingComputer
The site is offering a file called Installer.zip that contains an executable that appears to be corrupt and does not infect users with any malware.
However, MalwareHunterTeam, who first discovered this malicious site, found other malicious files distributed by the site that allowed us to see what malware it was spreading.
One of the files distributed by this malicious site is setup.zip, which contains the setup.lnk file. Setup.lnk is a Windows shortcut that will execute a PowerShell command to download a system32.hta file from pixelmon[.]pw.
Source: BleepingComputer
When BleepingComputer tested these malicious payloads, the System32.hta file downloaded Vidar, a password-stealing malware that is not as commonly used as it was in the past. This was confirmed by security researcher Fumik0_, who has previously analyzed this malware family.
When executed, the threat actor's Vidar sample will connect to a Telegram channel and retrieve the IP address of a malware's command and control server.
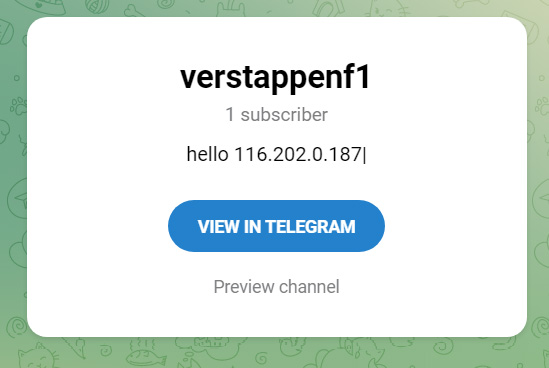
Source: BleepingComputer
The malware will then retrieve a configuration command from the C2 and download further modules to be used to steal data from the infected device.
The Vidar malware can steal passwords from browsers and applications and search a computer for files that match specific names, which are then uploaded to the threat actor.
As you can see from the malware configuration below, the C2 instructs the malware to search for and steal various files, including text files, cryptocurrency wallets, backups, codes, password files, and authentication files.
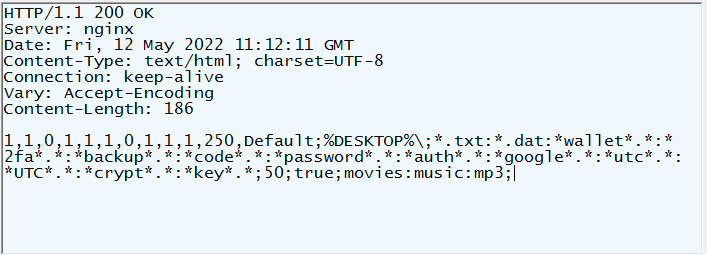
Source: BleepingComputer
As this is an NFT site, the expectation is that visitors will have cryptocurrency wallets installed on their computers. Due to this, the threat actors emphasize searching for and stealing files related to cryptocurrency.
While the site is currently not distributing a working payload, BleepingComputer has seen evidence that the threat actors continue to modify the site over the past few days, as payloads that were available two days ago are no longer present.
Due to the activity on the site, we can expect this campaign to continue to be active and for working threats to be added soon.
With NFT projects being overwhelmed with scams designed to steal your cryptocurrency, you should always triple-check that the URL you are visiting is, in fact, related to the project you are interested in.
Furthermore, never execute any executables from unknown websites without first scanning them with antivirus software or using VirusTotal.



Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now